Design Thinking: A Non-Linear Process
Design thinking is a human-centered approach to problem-solving that is transforming the way designers and organizations approach innovation. By placing the needs and experiences of users at the forefront of the design process, designers can create solutions that are not only functional and effective but also meaningful and engaging.
What is Designing Thinking?
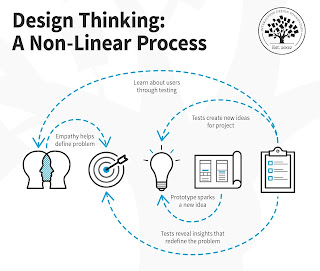
Design thinking is a problem-solving approach that focuses on understanding the needs and perspectives of users or customers in order to develop innovative solutions. It is a process that involves empathizing with the user, defining the problem, ideating and brainstorming potential solutions, prototyping and testing those solutions, and iterating until a viable solution is found.
Design thinking can be used in a variety of contexts, from developing new products or services to improving processes or systems. It is often used in fields such as product design, software development, and business strategy.
One of the key principles of design thinking is empathy, which involves putting the designer himself in the shoes of the user or customer to understand their needs, wants, and pain points. This empathy helps to inform the design process and ensures that the resulting solution meets the user's needs.Design thinking also emphasizes iteration and prototyping, which means testing out potential solutions in small-scale, low-risk ways and using feedback to refine and improve the design. This approach helps to minimize the risk of investing time and resources into a solution that ultimately does not work well for the user.
Overall, design thinking is a user-centred, iterative approach to problem-solving that emphasizes empathy, creativity, and experimentation.
There are many tools and methods used in design thinking. The key is to find the tools that work best for the team and the problem that the designer is trying to solve. Some of the most common ones include:
Empathy mapping: This tool is used in design thinking to help teams gain a deeper understanding of their users' needs, behaviours, and motivations. Here are some empathy mapping tools that can be used:
Miro: Miro is a collaborative online whiteboarding platform that has a template for empathy mapping. It allows team members to work together in real-time to create and refine empathy maps.
Lucidchart: Lucidchart is a visual workspace that allows teams to create and share diagrams, flowcharts, and other visualizations. It has a template for empathy mapping that can be used to capture user insights and share them with the team.
XPLANE: XPLANE is a visual thinking company that offers an empathy mapping template that can be downloaded and printed out. It includes prompts for capturing user needs, behaviours, and emotions.
Canva: Canva is a graphic design tool that offers a template for empathy mapping. It allows teams to create visually engaging empathy maps that can be easily shared and presented.
Sketch: Sketch is a design tool that offers a plugin called "Empathy Sketch" for creating empathy maps. It allows teams to create and collaborate on empathy maps within the Sketch app.
User personas: User personas are fictional characters that represent the different types of people who might use a product or service. They help designers to keep the user at the centre of the design process.
Xtensio: Xtensio is a collaborative visual workspace that offers a template for creating user personas. It allows teams to create and share personas with each other and with stakeholders.
Userforge: Userforge is a web-based tool for creating user personas. It offers a simple interface for creating and editing personas, and allows teams to share and collaborate on their work.
Persona.ly: Persona.ly is a tool for creating and managing user personas. It offers a variety of customization options, including the ability to add photos and detailed descriptions of users.
Smaply: Smaply is a user journey mapping tool that also offers a persona builder. It allows teams to create personas based on user research and insights, and to share and collaborate on their work.
Canva: Canva is a graphic design tool that offers a template for creating user personas. It allows teams to create visually engaging personas that can be easily shared and presented.
Journey mapping: Journey mapping is a process of mapping out the steps that a user takes when interacting with a product or service. It helps designers to identify pain points and opportunities for improvement.
Miro: Miro is a collaborative online whiteboarding platform that offers a template for journey mapping. It allows teams to work together in real-time to create and refine journey maps.
Lucidchart: Lucidchart is a visual workspace that allows teams to create and share diagrams, flowcharts, and other visualizations. It has a template for journey mapping that can be used to capture user experiences and identify pain points and opportunities for improvement.
Smaply: Smaply is a user journey mapping tool that offers a variety of templates and tools for creating and analyzing user journeys. It allows teams to collaborate on journey maps and share them with stakeholders.
Canva: Canva is a graphic design tool that offers a template for journey mapping. It allows teams to create visually engaging journey maps that can be easily shared and presented.
UXPressia: UXPressia is a user journey mapping tool that offers a variety of templates, including templates for customer journey maps, service blueprints, and personas. It allows teams to create and collaborate on journey maps and share them with stakeholders.
Ideation techniques: There are many ideation techniques used in design thinking, including brainstorming, mind mapping, and SCAMPER.
Brainstorming: Brainstorming is a technique that involves generating a large number of ideas in a short amount of time. It can be done individually or in a group, and can be facilitated by a moderator.
Mind mapping: Mind mapping is a visual tool used to organize and generate ideas. It involves creating a central idea and branching out with related ideas.
SCAMPER: SCAMPER is an ideation technique that involves asking a series of questions to stimulate creative thinking. The questions are: Substitute, Combine, Adapt, Modify, Put to another use, Eliminate, and Reverse.
Design thinking games: Design thinking games are interactive activities that encourage creativity and collaboration. Examples include "Crazy Eights," "Word Association," and "What if?"
Ideation workshops: Ideation workshops are structured sessions designed to generate and develop new ideas. They typically involve a facilitator who guides participants through a series of exercises and activities.
Random Word Generator: Random Word Generator is a tool that provides random words that can be used as prompts for generating new ideas.
Collaborative tools: Collaborative tools such as Miro, Google Docs, and Microsoft Teams allow teams to work together in real-time, no matter where they are located, to generate and develop new ideas.
Prototyping: Prototyping involves creating low-fidelity or high-fidelity models of a product or service to test and refine ideas.
Sketch: Sketch is a digital design tool used to create mockups and wireframes for websites and mobile apps. It is a popular tool for creating user interface (UI) designs and can be used to quickly create and test prototypes.
Figma: Figma is a collaborative interface design tool that allows teams to create, share, and test prototypes in real-time. It offers a range of features and integrations, including design libraries, plugins, and collaboration tools.
InVision: InVision is a digital product design platform that offers tools for prototyping, collaboration, and design management. It allows teams to create and test interactive prototypes, share feedback, and track design changes.
Marvel: Marvel is a web-based platform that allows designers to create and test interactive prototypes for web and mobile apps. It offers a range of features, including design tools, collaboration tools, and integrations with other design tools.
Adobe XD: Adobe XD is a user experience (UX) design tool that allows designers to create wireframes, mockups, and prototypes for websites and mobile apps. It offers a range of features, including design tools, prototyping tools, and collaboration tools.
Balsamiq: Balsamiq is a tool used to create low-fidelity wireframes and mockups. It is designed to be quick and easy to use, allowing designers to quickly create and test ideas before moving on to high-fidelity designs.
Axure: Axure is a tool used for creating interactive prototypes for websites and mobile apps. It allows designers to create complex interactions and animations and offers a range of features for collaboration and design management.
Sketchflow: Sketchflow is a tool used to create interactive prototypes for Microsoft Silverlight and Windows Presentation Foundation (WPF) applications. It allows designers to quickly create and test prototypes without writing code.
Testing and iteration: Design thinking is an iterative process, which means that designers test their ideas with users and make changes based on their feedback. It is a critical phase in the design thinking process that involve evaluating and refining prototypes to improve their usability and effectiveness.
User testing software: User testing software, such as UserTesting and Validately, allows designers to conduct remote user testing sessions to gather feedback and insights about their prototypes. These tools typically provide a way to record users' interactions and capture their feedback through surveys or interviews.
A/B testing software: A/B testing software, such as Optimizely and Google Optimize, allows designers to test different variations of their designs with users to determine which performs best. These tools typically provide a way to track user behavior and analyze data to identify trends and insights.
Analytics software: Analytics software, such as Google Analytics and Adobe Analytics, allows designers to track and analyze user behavior on websites and mobile apps. This data can be used to identify usability issues and opportunities for improvement.
Heat mapping software: Heat mapping software, such as Crazy Egg and Hotjar, allows designers to visualize user behavior on websites and mobile apps. Heat maps show where users are clicking, scrolling, and spending time on a page, providing insights into how to improve the design.
Feedback and collaboration tools: Feedback and collaboration tools, such as Slack and Trello, allow teams to communicate and collaborate on design projects. These tools can be used to share feedback, track progress, and manage tasks related to testing and iteration.
Prototyping software: Prototyping software, such as Sketch and InVision, allows designers to create and test prototypes quickly and easily. These tools provide a way to iterate on designs and gather feedback from users before moving on to development.
Design systems and style guides: Design systems and style guides, such as Material Design and Bootstrap, provide a set of standards and guidelines for designing and building user interfaces. These tools can be used to ensure consistency across designs and improve usability.
Design sprints: A design sprint is a five-day process that helps teams to rapidly prototype and test ideas.
Whiteboards and sticky notes: Whiteboards and sticky notes are a common tool used in design sprints for brainstorming and organizing ideas. Teams can use these tools to visually map out the problem space, generate ideas, and prioritize solutions.
Design thinking frameworks: Design thinking frameworks, such as the double diamond, help teams structure their design sprints and ensure they are following a consistent process. These frameworks provide a roadmap for the design sprint and help teams stay on track.
Sprint planning tools: Sprint planning tools, such as Trello and Asana, can be used to manage the logistics of the design sprint. Teams can use these tools to set goals, assign tasks, and track progress throughout the sprint.
Prototype and testing tools: Prototype and testing tools, such as InVision and Marvel, can be used to quickly create and test prototypes during the design sprint. These tools provide a way to iterate on designs and gather feedback from users before moving on to development.
Collaboration and communication tools: Collaboration and communication tools, such as Slack and Zoom, are essential for remote design sprints. These tools allow team members to communicate and collaborate in real-time, regardless of their location.
Mind mapping tools: Mind mapping tools, such as MindMeister and Coggle, can be used to visually map out the problem space and generate ideas during the design sprint. These tools provide a way to organize and prioritize ideas and ensure the team is aligned around the problem they are trying to solve.
Post-it capture tools: Post-it capture tools, such as Miro and Stormboard, can be used to capture and organize ideas generated during the design sprint. These tools provide a way to collaborate and iterate on ideas remotely.
Design principles: Design principles are a set of guidelines that help designers make decisions about how to create products and services that are functional, user-friendly, and aesthetically pleasing.
Design guidelines and standards: Design guidelines and standards, such as Apple's Human Interface Guidelines or Google's Material Design Guidelines, provide a set of design principles and best practices for creating user-friendly and consistent interfaces across different platforms.
Design frameworks and models: Design frameworks and models, such as the Design Sprint or the Double Diamond Model, provide a structured process for designing and solving complex problems. These frameworks help ensure that designers are following a consistent and effective process.
User research tools: User research tools, such as surveys, interviews, and focus groups, help designers gain a deeper understanding of their users' needs, behaviors, and preferences. This information is essential for creating effective and user-friendly products and services.
Feedback and collaboration tools: Feedback and collaboration tools, such as Slack and Asana, allow designers to share their work and collaborate with team members to ensure that their designs are aligned with the overall project goals.
Prototyping and testing tools: Prototyping and testing tools, such as Sketch and InVision, help designers quickly create and test prototypes of their designs with users. This feedback allows designers to iterate on their designs and make improvements before moving on to development.
Design thinking workshops: Design thinking workshops, such as those offered by IDEO and other design firms, provide hands-on training and experience in using design principles and tools to solve complex problems.
Design thinking courses and certifications: Design thinking courses and certifications, such as those offered by the Stanford d.school or the Interaction Design Foundation, provide a comprehensive education in the principles and practices of design thinking.
Visual thinking: Visual thinking is a technique that involves using visual aids like diagrams, sketches, and flowcharts to communicate ideas and concepts to stakeholders and users.
Sketching and drawing tools: Sketching and drawing tools, such as pencils, markers, and digital drawing software like Adobe Illustrator or Procreate, allow designers to quickly sketch out their ideas and communicate them visually.
Mind mapping tools: Mind mapping tools, such as MindMeister or XMind, allow designers to visually map out complex concepts and relationships between ideas. These tools can help designers organize their thoughts and identify new opportunities for exploration.
Diagramming tools: Diagramming tools, such as Microsoft Visio or Gliffy, allow designers to create flowcharts, wireframes, and other visual representations of their ideas. These tools can be used to explore user journeys, map out workflows, and create low-fidelity prototypes.
Storyboarding tools: Storyboarding tools, such as Storyboarder or Boords, allow designers to create visual narratives that explore different user scenarios and interactions. These tools can help designers identify key moments in the user experience and develop effective storytelling techniques.
Visual collaboration tools: Visual collaboration tools, such as Mural or Miro, allow teams to collaborate and brainstorm ideas visually in real-time. These tools can be used to facilitate virtual brainstorming sessions, workshops, and design sprints.
Data visualization tools: Data visualization tools, such as Tableau or Infogram, allow designers to create compelling visualizations of complex data sets. These tools can be used to communicate insights and findings in a clear and accessible way.
Animation and video tools: Animation and video tools, such as Adobe After Effects or Final Cut Pro, allow designers to create dynamic and engaging visual content. These tools can be used to create user demos, explainer videos, and other multimedia assets that help communicate complex ideas and concepts.
Design thinking is a powerful methodology that allows designers to create user-centric and innovative solutions to complex problems. In this blog post explores the various tools and techniques used in the design thinking process, from empathy mapping and user personas to prototyping and testing. It also discusses the importance of visual thinking and the tools used to support it, such as sketching and drawing tools, mind mapping tools, and data visualization tools.
By using these tools and techniques, designers can gain a deeper understanding of their users' needs and preferences, explore new ideas and opportunities, and create effective and user-friendly products and services. The design thinking process is not a linear one, but rather a cyclical process that involves iterating on ideas and feedback until a final solution is reached.
Ultimately, the key to successful design thinking is to remain flexible, open-minded, and collaborative. By working closely with users, stakeholders, and team members, designers can create solutions that are not only functional and effective but also empathetic and engaging. The tools and techniques discussed in this post are just a starting point for designers looking to explore the possibilities of design thinking and create solutions that make a real difference in the world.
Cheers,
Venkat Alagarsamy




If you're looking for a comprehensive and top-notch machine learning training institute in Delhi, look no further than APTRON. As a leading IT training institute, APTRON offers a wide range of courses to help individuals and organizations alike to stay at the forefront of technological advancements in Machine Learning Training Institute in Delhi
ReplyDelete