Data Professionals: Unveiling the Key Roles and Specialties
In today's data-driven world, where information is king, the demand for skilled professionals who can extract valuable insights from data is skyrocketing. Data professionals play a vital role in unraveling the hidden stories within vast amounts of information, empowering organizations to make informed decisions and drive innovation. Whether you aspire to pursue a career in data or collaborate with data experts, understanding the different roles and specialties within this field is crucial.
This blog post explores the key roles and responsibilities of data professionals, their areas of business applications, and the tools, applications, and libraries they utilize to drive data-driven decision-making. Whether you're a CEO, CTO, data scientist, or software engineer, understanding the different roles within the data profession will help you leverage the power of data effectively.
Let's understand the roles of each data management specialist and what kind of tools and frameworks they use and highlight areas of applications:
Areas of Applications
Data Analyst
Marketing: Data analysts can analyze customer demographics, purchasing behavior, and campaign performance to optimize marketing strategies and target specific customer segments effectively.
Supply Chain Management: Data analysts can analyze supply chain data to identify bottlenecks, optimize inventory levels, and improve overall efficiency.
Customer Service: By analyzing customer feedback and support interactions, data analysts can identify patterns and trends, leading to improved customer service processes and enhanced customer satisfaction
Data Architect
E-commerce: Data architects can design scalable and robust data architectures to handle large volumes of transactional data, ensuring seamless shopping experiences and efficient order processing.
Telecom: Data architects can design data systems that integrate call detail records, network performance data, and customer information, enabling telecom companies to optimize network infrastructure, improve service quality, and offer personalized plans
Energy: Data architects can design data integration systems that consolidate data from smart grids, energy meters, and weather forecasts, facilitating demand forecasting, energy optimization, and efficient energy distribution.
Data Scientist
Fraud Detection: Data scientists can develop predictive models to identify fraudulent activities in financial transactions, enabling timely intervention and minimizing financial losses.
Healthcare: Data scientists can analyze patient data, medical records, and genetic information to develop personalized treatment plans, predict disease outcomes, and improve patient care.
Transportation: Data scientists can use data from sensors, GPS devices, and historical traffic patterns to optimize transportation routes, reduce congestion, and improve logistics efficiency.
Data Engineer
Social Media: Data engineers can build data pipelines to collect and process vast amounts of social media data, enabling companies to gain insights into customer sentiments, brand perception, and campaign effectiveness.
IoT (Internet of Things): Data engineers can design and implement data architectures to handle the massive influx of data from IoT devices, facilitating real-time analysis and enabling predictive maintenance in industries like manufacturing and utilities.
Finance: Data engineers can develop robust data infrastructure to handle high-frequency trading data, ensuring fast and accurate processing for algorithmic trading systems.
Business Intelligence (BI) Developer
Retail: BI developers can create interactive dashboards that provide real-time sales data, inventory levels, and customer insights, helping retailers monitor performance, optimize pricing strategies, and identify opportunities for cross-selling or upselling.
Human Resources: BI developers can develop HR analytics dashboards to track employee performance, engagement levels, and turnover rates, enabling HR departments to make data-driven decisions regarding talent management and retention strategies.
Education: BI developers can create dashboards that provide insights into student performance, course engagement, and learning outcomes, helping educators identify areas for improvement and personalize instruction.
Machine Learning Engineer
Image Recognition: Machine learning engineers can develop algorithms that accurately classify and analyze images, enabling applications such as autonomous vehicles, facial recognition systems, and quality control in manufacturing.
Natural Language Processing: Machine learning engineers can build language models and sentiment analysis systems, improving chatbots, virtual assistants, and automated customer support systems.
Financial Risk Assessment: Machine learning engineers can develop models that assess credit risk, detect anomalies in financial transactions, and predict market trends, assisting financial institutions in making informed investment decisions.
Data Privacy and Security Specialist
Healthcare: Data privacy and security specialists can implement strict access controls, data anonymization techniques, and encryption protocols to protect patient data and comply with strict healthcare regulations.
Legal: Specialists in data privacy and security can help law firms ensure data confidentiality, implement secure document management systems and protect client information from unauthorized access or data leaks.
Technology: Data privacy and security specialists can assist technology companies in implementing robust security measures for cloud storage, securing customer data, and addressing vulnerabilities in software applications.
Conclusion
The world of data professionals is vast and dynamic, comprising various roles and specialties. Each role brings unique skills, responsibilities, and tools to the table, contributing to the extraction of insights and value from data. From data analysts uncovering trends to data scientists creating predictive models, and from data engineers building robust infrastructures to BI developers enabling data-driven decision-making, these professionals play vital roles in driving business success and innovation.
Their expertise empowers organizations across industries to optimize processes, improve customer experiences, and gain a competitive edge. By understanding the different roles and responsibilities within the data profession, businesses can leverage the power of data effectively, drive innovation, and navigate the data-driven landscape successfully.

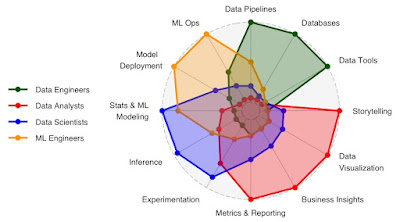



Good attempt and thanks for drawing this simple classification. But I am surprised that the notion of DataOps is missing here (or defined partially but discretely). I am also of the opinion that the Modern MLops and MLaaS encompasses the notion of DataOps.
ReplyDeleteThank you for your valuable feedback. I completely agree that DataOps is an essential concept that often goes overlooked. The intention of this blog post was to highlight the key roles and responsibilities of data professionals in managing large-scale data environments.
DeleteIt sounds like you have a great idea for another blog post that delves into the distinctions between DevOps, MLOps, DataOps (as a subset of MLOps), and AIOps. Such an article would provide valuable insights into these related disciplines.
Indeed, modern MLOps and MLaaS encompass the principles and practices of DataOps. Many of the tools and techniques used in DataOps are shared with MLOps. For instance, both disciplines make use of version control, continuous integration, and continuous delivery (CI/CD).
The main distinction between DataOps and MLOps lies in their focus. DataOps covers the entire data lifecycle, including data collection, analysis, and deployment. On the other hand, MLOps concentrates on the lifecycle of machine learning models, encompassing their development, deployment, and monitoring.
Considering both DataOps and MLOps is crucial when working with machine learning models. By combining the best practices from both disciplines, we can create more robust and scalable machine learning solutions.
Once again, thank you for your feedback and valuable insights. I appreciate your contribution. If you have any further questions, feel free to ask.
More read: https://venkat-alagarsamy.blogspot.com/2023/05/power-of-devops-devsecops-and-mlops-in.html
DeleteNice article. Thanks for sharing.
ReplyDeleteMLOps Training
MLOps Course in Hyderabad
MLOps Online Course
MLOps Online Training
Machine Learning Operations Training
MLOps Training in Hyderabad
MLOps Training Course
MLOps Training Online
MLOps Training in India
MLOps Course in Ameerpet
MLOps Training in Bangalore
MLOps Training Course in Chennai